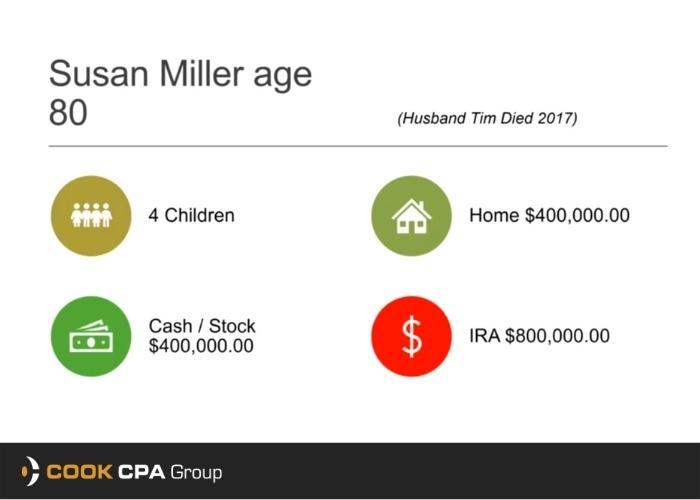
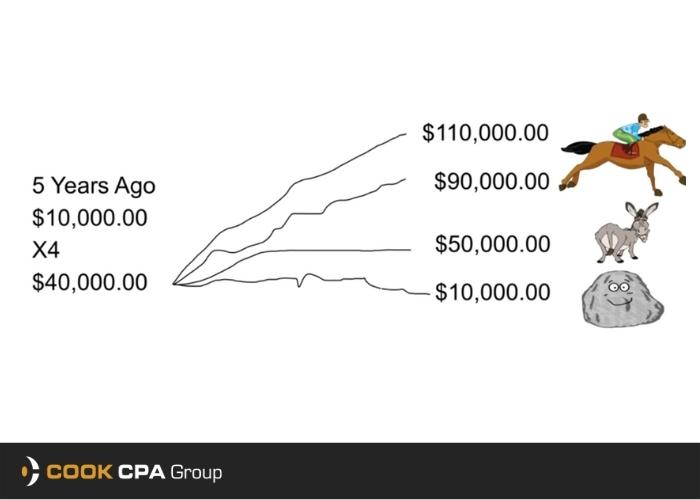
As a mid-sized business, you know how difficult it can be to stay on top of your accounting. With employees to manage, fires to put out, and a healthy work-life balance to maintain, making time to keep on top of your accounting practices is more complicated than ever.
As you grow your company and employee base, staying on top of your accounting operations becomes increasingly important. This post will guide you through five strategic accounting tips your mid-sized business can use today, including:
- Maintaining business records
- Defining an accounting strategy
- Automating accounting practices
- Leveraging business tax credits
- Outsourcing your accounting practice
Strategic Accounting Tip #1: Maintain Updated Business Records
The first strategic accounting tip for your mid-sized business is to maintain accurate and updated business records. Recordkeeping is an essential function of any business and a critical component of complying with IRS accounting requirements. There are three main accounting areas to pay particular attention to as you strive to maintain accurate business records.
- Gross income
The most straightforward business recordkeeping responsibility is tracking gross receipts or gross income. This is the income your business generates. Make sure to maintain accurate records of sales in the form of deposit receipts from both credit card and cash sales, any invoices
- Expenses
Expenses are all the costs you incur running your business, including payments and transfers. Consider using accounting software that automatically keeps track of this type of business record for easy accounting during tax season.
- Assets
Calculating the annual depreciation of your business fixed assets is an important recordkeeping practice. Ensure you maintain original asset documents, including purchase and sales receipts, as well as any proof of payment documents to make your business accounting run as smoothly as possible.
Strategic Accounting Tip #2: Decide on Your Accounting Strategy and Stick With It

Once you have a handle on your recordkeeping habits, the next strategic accounting tip your mid-sized business should leverage is deciding on one accounting practice and sticking with it. Choosing between accrual accounting and cash basis accounting is a matter of preference.
While cash basis accounting tends to be easier for small and mid-sized businesses, accrual accounting is used most often.
The difference between the methods comes down to the way expenses are deducted. In cash basis accounting, revenue is documented as soon as payment is received. Conversely, accrual accounting records revenue when the product or service is delivered.
At Cook CPA Group, we recommend your business align with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) by using the accrual accounting method. In addition to being the most common accounting method for mid-sized businesses, accrual accounting provides a general overview snapshot of your business. This can be very helpful in determining the financial health of your business.
Strategic Accounting Tip #3: Automate Accounting Practices
You may reach a point in your mid-sized business where manual accounting practices are no longer efficient or productive for your team. Automating basic accounting practices for your business is a strategic tip you can leverage today.
Finding the appropriate accounting software for your business can be challenging, but once you select and install it, keeping your financial books in order is a breeze. To determine the right software or accounting automation plan for you, consider which accounting processes you can automate.
You may need to consider your company’s existing technology and the necessary training to ensure your staff has the know-how to use automation software. It’s also important to involve your team in the automation process. Make sure the entire team knows expectations for recordkeeping and basic troubleshooting processes.
Consider automating these accounting practices to keep your company’s finances running like clockwork:
- Accounts payable
- Accounts receivable
- Payroll
- Credit card and bank statements
- Account and statement reconciliation
- Routine banking tasks like transfers and monthly payments
- Financial reporting and tax compliance functions
Automation for your accounting tasks is one of the best steps you can take for your mid-sized business. Stop wasting precious time and overcome year-end hassles by automizing your business accounting process today.
Strategic Accounting Tip #4: Leverage Business Tax Deductions

As a mid-sized business owner, you’re no stranger to tax deductions. And while it’s easier to put off recording those business deductions until right before tax season, our recommendation is to figure out the deductions you can leverage before tax season.
There are plenty of tax deductions your mid-sized company can take advantage of to reduce your tax burden. The trick is to ensure your strategy for keeping the appropriate accounting records for each business expense.
The most common business tax deductions your mid-sized business can leverage are labor costs and operating expenses. Payroll and administrative expenses to the equipment you use on a daily basis are common tax deductions you’re likely already aware of.
However, other business expenses like marketing and advertising can be claimed on your tax form as deductible expenses so long as you retain the appropriate records. Another deductible your mid-sized company may not think to leverage is the payment for professional services. Payments to accountants, lawyers, and even professional membership networks can and should be leveraged deductions at tax time.
With the right accounting practices in place, you can appropriately document and justify these business expenses to save big this tax year.
Strategic Accounting Tip #5: Outsource Accounting
Outsourcing your accounting tasks to a professional accounting group is a great way to save time and an easy way to save your company money. Rather than hiring and training new employees to perform basic accounting functions, outsource your business accounting functions to a trusted professional.
Remember, hiring a professional service provider like an accountant to help with business tax is an eligible deduction come tax time! Save yourself the headache of getting your financial records in order and filing your taxes the right way.
Expert business accountants like Cook CPA Group can help you file federal corporate taxes and save you money on your tax bill. With decades of professional accounting experience, we can efficiently and accurately help you file your mid-sized company’s federal corporate tax.
Schedule a free consultation today if you’re ready to leave the important accounting functions to the pros.